Support for Technology Providers
Research in agronomy and agriculture produces new, improved technologies with the potential to increase yields, resist pests and diseases, withstand adverse climates, improve nutrition and income, and more. The TAAT e-catalogs are a powerful step on the road towards such impact:
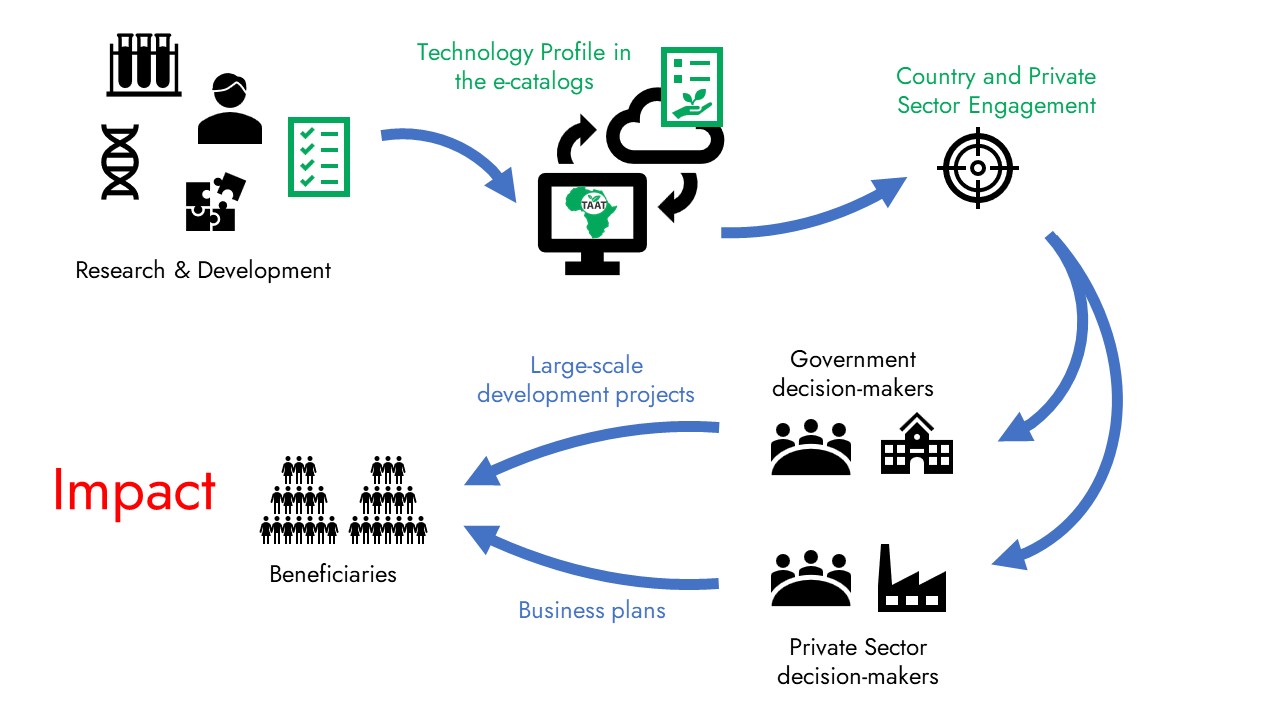
Technology Providers are researchers or representatives of organizations that own technologies that we showcase on the e-catalogs. They own the data we publish on their technologies in the e-catalogs.
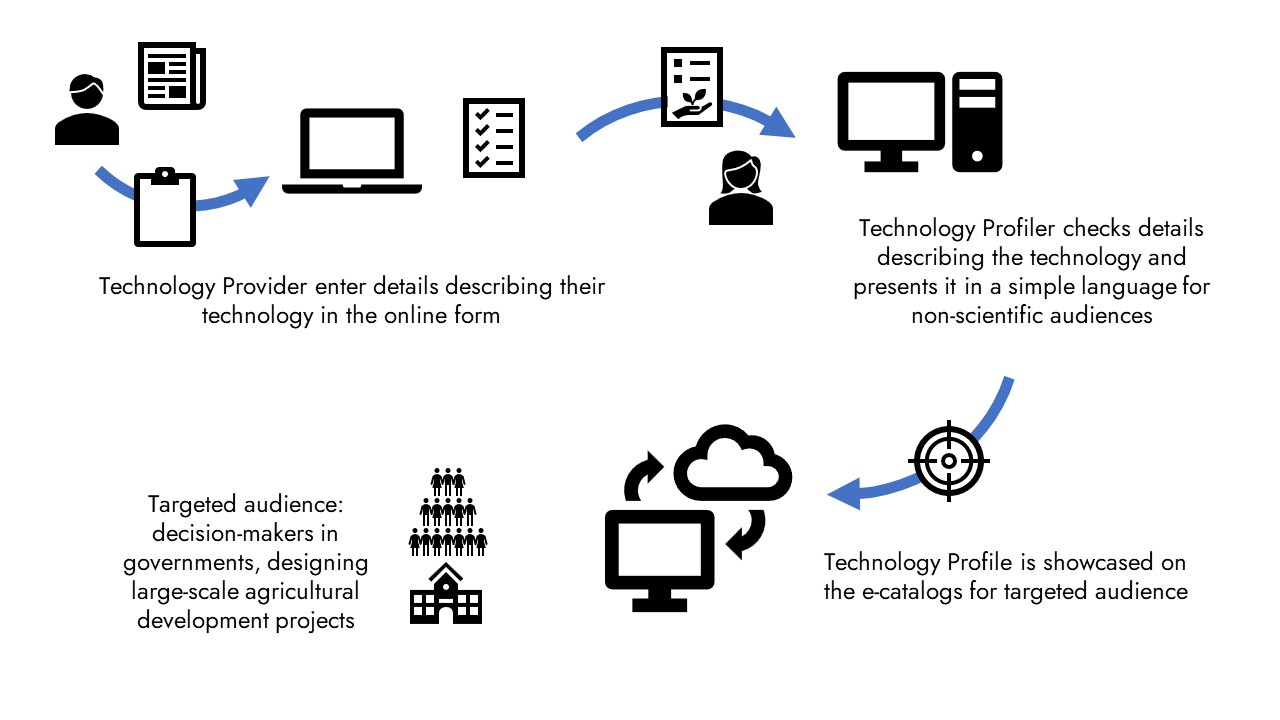
Technology Providers work with the TAAT technology Profiling team to create technology profiles that are customized to the needs of the audience of the e-catalogs:
-
- decision-makers in governments, who are responsible for the design and implementation of large-scale agricultural development projects,
- decision-makers in private sector companies, who are responsible for the integration of agricultural technologies in new or improved business plans,
- decision-makers in international finance institutions funding agricultural development, or in large international organizations such as iNGOs, responsible for designing and implementing large-scale agricultural development programs.
We provide here supporting and guiding material for Technology Providers:
- e-learning course: introduction to the e-catalogs.
- This e-learning course takes under 5 minutes to study and gives you an easy-to-follow overview of the e-catalogs and technology profiles, their objective and their audience.
- Save the file on your computer and double-click on it, it is then automated and interactive.
- Overview of the process for the creation of a new Technology Profile.
- Guide on the use of the online form.
Latest technologies
Structure, Trace, Scale & Connect with Solutions eProd is a digital supply chain management platform designed for agriculture. It helps organizations register farmers, monitor production, ensure traceability, and manage payments efficiently. The system is modular, works offline, and integrates easily with other digital tools.
Digital transparency and incentives for resilient landscape restoration My Farm Trees (MFT) is a digital platform that supports the restoration of forest landscapes by ensuring complete traceability, from seed collection to tree growth, using blockchain technology. It combines three mobile applications dedicated to seed collection, nursery management, and planting monitoring. Connected to a central dashboard, it guarantees quality control and data verification and facilitates digital payments to reward those involved in restoration. Developed by the Bioversity International Alliance and CIAT, MFT promotes the use of local species, improves livelihoods, and contributes to climate resilience. After Cameroon and Kenya, the platform is now being extended to other countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
With QualiSani, no more toxic compounds such as Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in your smoked fish and grilled meat, and reduction of cancer risk for consumers. Traditional methods of grilling and smoking food, particularly in African countries, have long been associated with health risks due to the formation of harmful compounds such as Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). These carcinogenic substances are produced when food is exposed to smoke and high temperatures, and their presence in grilled and smoked products has raised significant public health concerns. Studies conducted in Benin country have revealed alarming levels of PAHs in smoked and grilled meats and fish, often exceeding international safety standards. This contamination is linked to the direct exposure of food to smoke, the type of fuel used (often wood), and the inefficient design of traditional processing equipment. The accumulation of PAHs not only poses a cancer risk to consumers but also hampers the marketability of these products in regions with stricter food safety regulations. Addressing this challenge requires innovations in food processing technologies that can reduce or eliminate the formation of PAHs while maintaining or improving the efficiency and productivity of the smoking and grilling process. The development of improved equipment, such as QualiSani, represents a significant step towards safer food processing practices. These advancements aim to protect consumers' health, enhance the quality of grilled and smoked products, and support the sustainable development of small to medium-sized food processing enterprises.